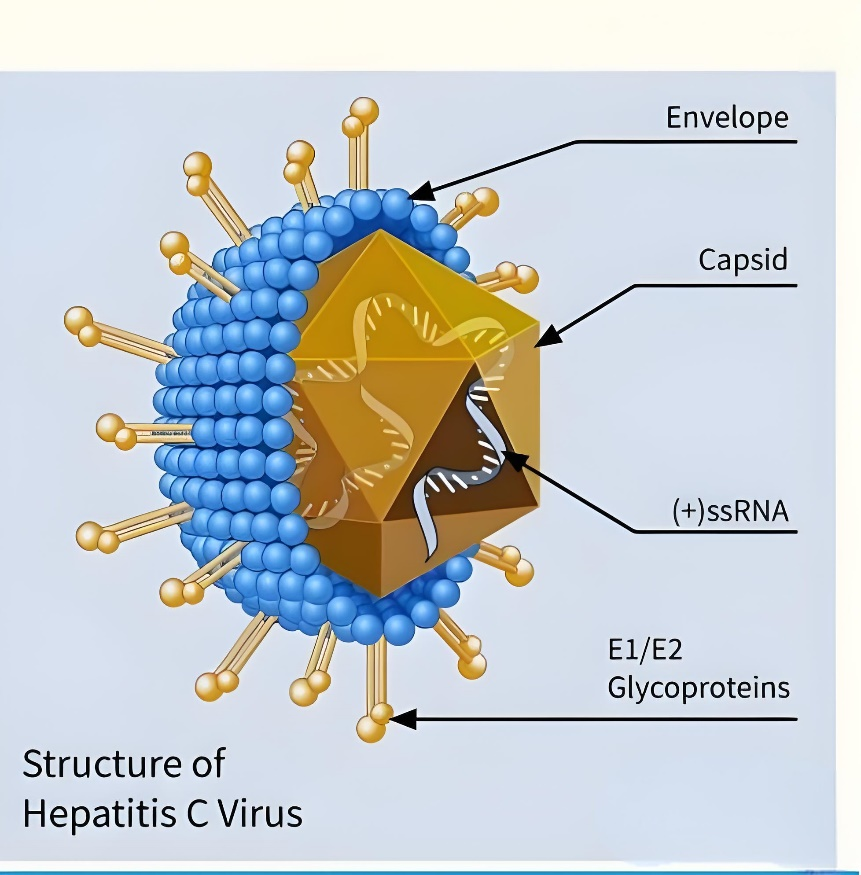
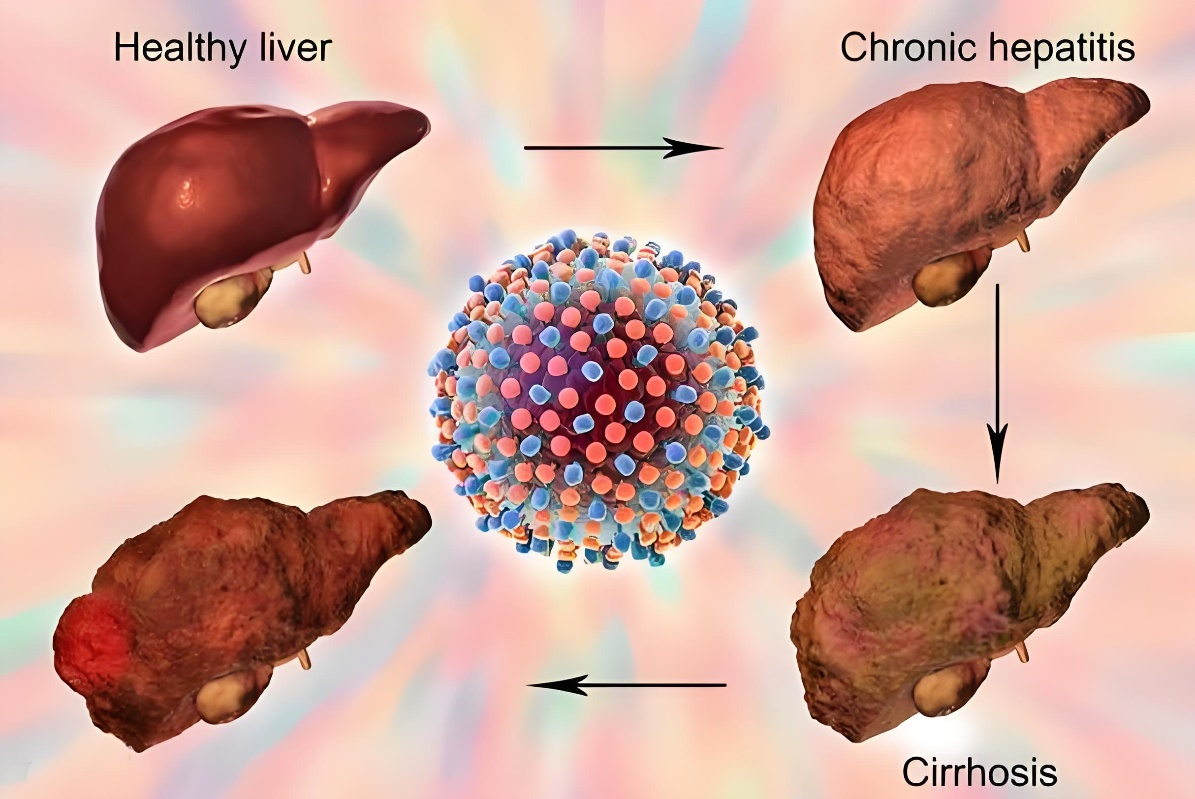
Hepatitis C, is a viral hepatitis caused by infection with the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The virus mainly attacks the liver, causing chronic inflammation, necrosis and fibrosis of the liver, and may even develop into cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatitis C has become a global public health problem, which has a serious impact on people’s health and quality of life.
You may not be so familiar with hepatitis C, but you must have heard of one of its brothers, hepatitis B. Hepatitis B and hepatitis C are both viral hepatitis, which are common hepatitis diseases in China. The pathogenesis of hepatitis B and hepatitis C is different. In China, only about 10% of hepatitis B will be converted from acute to chronic, while 50% of hepatitis C will be converted. Compared with hepatitis B, hepatitis C is more resistant and variable, and its progress is insidious (most people with hepatitis C have no symptoms).
Source:Public
Symptoms of Hepatitis C
The symptoms of hepatitis C may vary from individual to individual. In the acute infection period, most patients may not have obvious symptoms, or only show mild fatigue, poor appetite, yellow urine and so on. However, if the disease is not controlled in time, chronic hepatitis C may gradually develop. Symptoms of chronic hepatitis C include fatigue, bloating, dull abdominal pain, and indigestion. When the condition is serious, jaundice, gastrointestinal bleeding, hypersplenism and other symptoms may also occur.
Source: Baidu
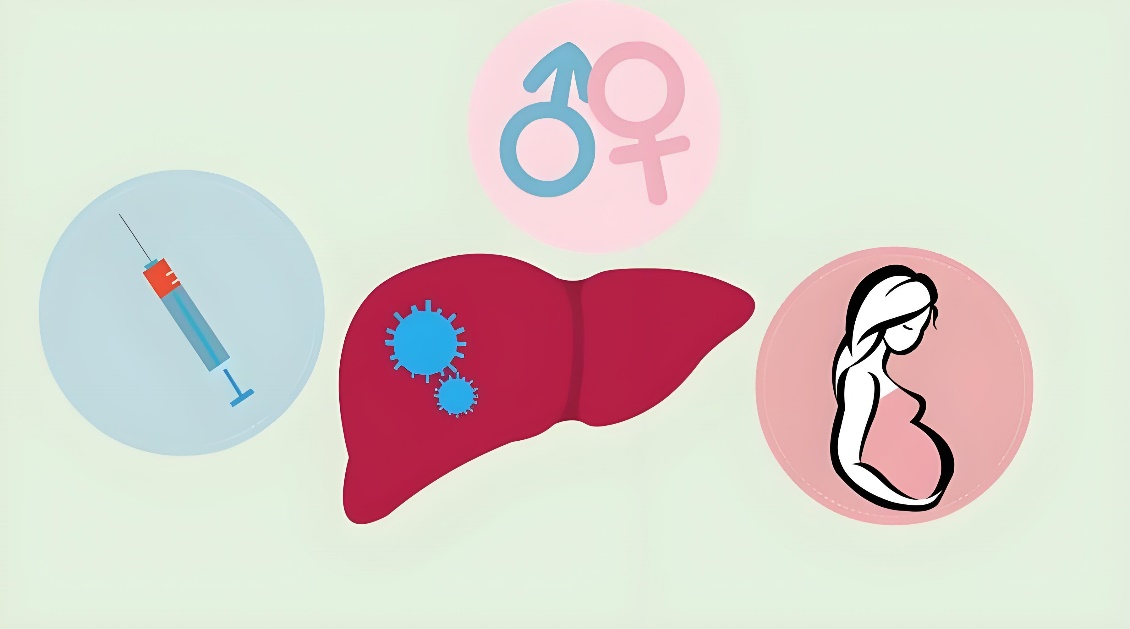
Transmission route of hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is mainly transmitted through blood, mother-to-child transmission and sexual transmission. Blood transmission is the most common mode of transmission, including blood transfusion, needle sharing, drug abuse and so on. Mother-to-child transmission refers to the transmission of hepatitis C virus from mother to child during pregnancy and childbirth. Sexual transmission is due to the close contact of body fluids and semen between men and women during sexual behavior, thus transmitting the virus.
How do I know I’m infected with hepatitis C?
1. Antibody (anti-HCV) qualitative detection
After the human body is infected with hepatitis C virus, the immune system will produce antibodies within 6 months, and the detection of anti-HCV can determine the immune response of the human body infected with hepatitis C virus. A positive HCV antibody test means that you have been infected with hepatitis C, but it may be a current HCV infection, a previous infection, or clearance of HCV after treatment. After the antibody test is positive, further nucleic acid testing is needed to determine whether it is a current infection state.
2. Nucleic acid (HCV RNA) detection
The results of quantitative detection of hepatitis C nucleic acid (HCV RNA) are the markers to determine whether the virus replicates after infection, reflecting the presence or absence, more or less of hepatitis C virus in the blood. If the quantitative test result of hepatitis C nucleic acid (HCV RNA) is positive, it indicates that hepatitis C is currently infected and there is hepatitis C virus replication in the body.
At present, only HCV antibody and HVC RNA are two major indicators for the detection of hepatitis C infection. It should be noted that, unlike hepatitis B antibody, HCV antibody is not a protective antibody, but a sign of hepatitis C virus infection. After HCV infection, about 65% to 80% of patients develop chronic HCV infection and rarely recover spontaneously. HCV RNA is suppressed or cleared if treated with effective antiviral therapy.
BoatBIo Data
Reagent: BoatBIo HCV antigen (CMIA)
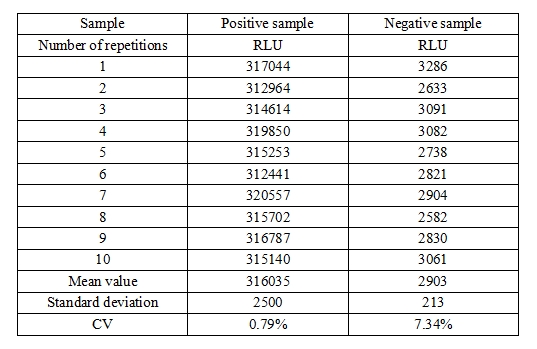
Precision: The precision of clinical samples containing positive and negative points was tested, and the coefficient of variation (CV) of the luminescence value (RLU) was less than 10%, and the precision of the bopeptide-HCV reagent is great.
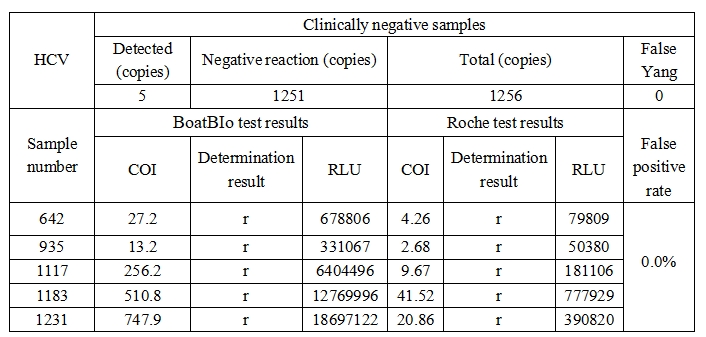
Specificity: 1256 random clinical samples were tested, and 5 positive cases and 1251 negative cases were detected. 5 positive cases were rechecked with Roche reagent (electrochemiluminescence method), and the results of Roche test were consistent with those of BoatBIo test. BoatBIo-HCV has low false positive rate and good specificity.
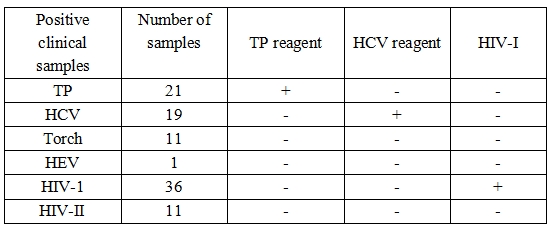
Cross reaction: TP, Torch, HEV and HIV-II positive samples were tested, and no cross reaction was found.
BoatBio Recommendation
Measures to prevent hepatitis C
1. Avoid unnecessary injection, blood transfusion and use of blood products; If these operations are needed, regular medical and health institutions should be selected to ensure the safety of the operation process.
2. Do not share needles or other tattoo and puncture tools with others, and do not share razors, toothbrushes and other personal articles that may cause bleeding with others.
3. Maintain sexual hygiene and use condoms correctly. Correct sex education should be given to teenagers, and those with a history of sexual disorder should be regularly examined and managed.
4. Women infected with hepatitis C virus should avoid pregnancy before they are cured. Postpartum hepatitis C patients should avoid breastfeeding if their nipples are damaged.
5. Dental instruments, endoscopes and other medical instruments should be strictly disinfected, and gloves should be worn when contacting blood and body fluids of hepatitis C patients.
Post time: Jun-25-2024