
Testing for influenza A or B is essential for effective flu management. It helps identify the specific virus type, enabling healthcare providers to recommend appropriate treatments. Tools like the Influenza A/B Rapid Test Kit offer quick and reliable results. Early detection through methods such as the Influenza A/B Rapid Test also aids in controlling virus transmission.
Key Takeaways
- Testing for flu A or B is important for proper care. Finding it early helps doctors give medicine quickly, aiding recovery.
- The Flu A/B Rapid Test Kit gives fast results, perfect for quick checks. Testing at home is easy and helpful for people.
- Knowing how accurate tests are helps you choose wisely. Molecular tests find more cases, but rapid tests are quicker and might miss some.
Types of tests for influenza A or B
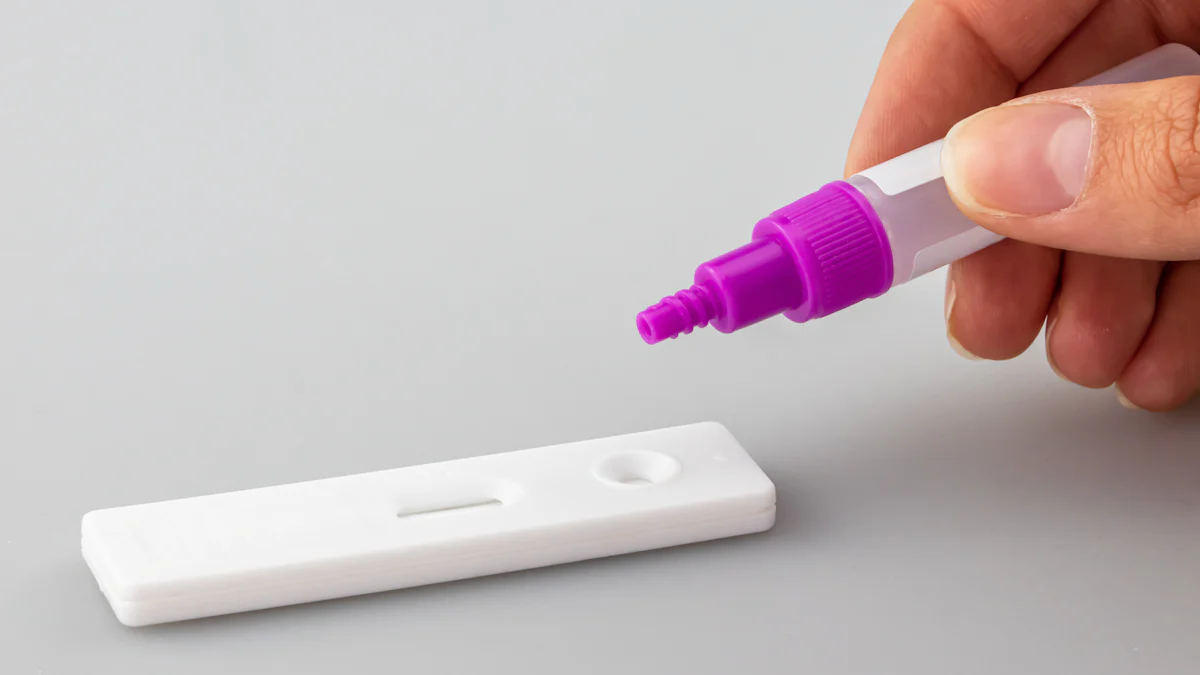
Influenza A/B Rapid Test Kit
The Influenza A/B Rapid Test Kit provides a quick and convenient way to detect influenza viruses. This test uses a nasal or throat swab to collect a sample, which is then analyzed for the presence of influenza A or B antigens. Results are typically available within 15 to 30 minutes, making it an ideal option for situations requiring immediate diagnosis. Many healthcare facilities rely on this test due to its speed and ease of use. The Influenza A/B Rapid Test Kit is also available for at-home use, offering individuals a practical solution for early flu detection.
Molecular assays
Molecular assays, such as reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), are highly sensitive and specific diagnostic tools. These tests detect the genetic material of influenza viruses, providing accurate results. Healthcare providers often use molecular assays in clinical settings to confirm cases of influenza A or B. Although these tests take longer to process than the Influenza A/B Rapid Test Kit, they offer superior accuracy. Molecular assays are particularly useful in identifying flu strains during outbreaks or for patients with severe symptoms.
Other diagnostic methods
Other diagnostic methods include viral culture and immunofluorescence assays. Viral culture involves growing the virus in a laboratory setting, which helps identify the specific strain. However, this method requires several days to produce results. Immunofluorescence assays detect viral antigens using fluorescent dyes, offering faster results than viral culture but with slightly lower accuracy. While these methods are less commonly used than the Influenza A/B Rapid Test Kit or molecular assays, they remain valuable in certain clinical scenarios.
How influenza tests are performed
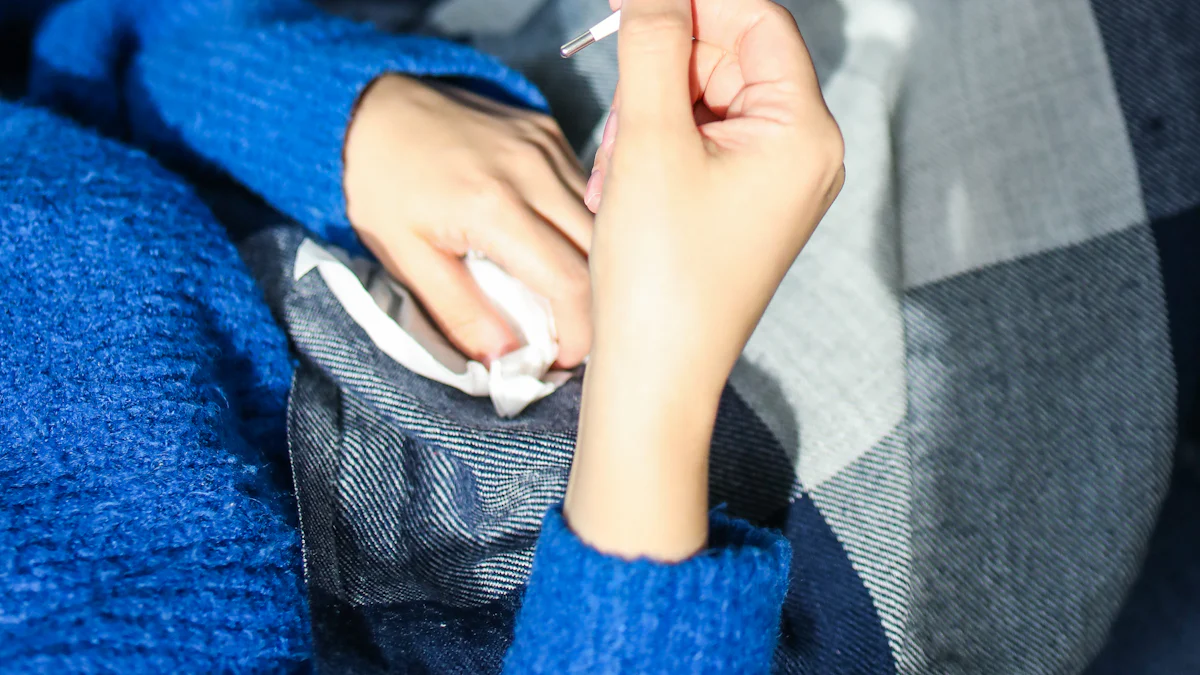

Clinical testing procedures
Healthcare professionals perform clinical influenza tests in controlled environments like hospitals or clinics. The process begins with sample collection, typically using a nasal or throat swab. The collected sample is then analyzed using diagnostic tools such as molecular assays or the Influenza A/B Rapid Test Kit. These tests detect the presence of influenza A or B viruses by identifying antigens or genetic material. Clinical testing ensures accurate results due to the expertise of trained personnel and the use of advanced equipment.
At-home testing options
At-home testing offers a convenient alternative for individuals unable to visit healthcare facilities. Many at-home kits, including the Influenza A/B Rapid Test Kit, allow users to collect nasal swab samples and obtain results within minutes. These kits include clear instructions, making them user-friendly for non-medical individuals. While at-home tests provide quick results, users should consult healthcare providers for confirmation if symptoms persist or worsen.
What to expect during testing
During influenza testing, individuals can expect a straightforward and quick procedure. For nasal swabs, a healthcare provider or the individual inserts a swab into the nostril to collect a sample. Throat swabs involve gently swabbing the back of the throat. The process may cause mild discomfort but is generally painless. Results from rapid tests are available within 15-30 minutes, while molecular assays may take longer. Understanding the procedure helps reduce anxiety and ensures a smooth experience.
Accuracy of influenza tests
Factors influencing accuracy
Several factors affect the accuracy of influenza tests. Timing plays a critical role. Tests conducted within the first three days of symptom onset yield the most reliable results due to higher viral loads. Sample collection techniques also influence accuracy. Proper swabbing of the nasal or throat area ensures sufficient viral material for testing. Additionally, the type of test used impacts precision. Molecular assays, for example, are more sensitive than rapid antigen tests. Environmental conditions, such as improper storage or handling of test kits, can further compromise results.
Comparing test accuracy
Different influenza tests vary in their accuracy. Rapid antigen tests, like the Influenza A/B Rapid Test Kit, provide results quickly but may have lower sensitivity. This means they might miss some positive cases. Molecular assays, including RT-PCR, offer higher sensitivity and specificity, making them more accurate in detecting influenza A or B. Viral culture, while highly precise, takes longer to deliver results and is less practical for immediate diagnosis. Comparing these methods highlights the trade-off between speed and accuracy, with molecular assays often considered the gold standard.
Understanding false positives and negatives
False positives and negatives can occur during influenza testing. A false positive indicates the presence of the virus when it is absent, often due to cross-reactivity with other pathogens. False negatives, on the other hand, fail to detect the virus despite its presence. These errors may arise from low viral loads, improper sample collection, or testing outside the optimal time frame. Understanding these limitations helps individuals interpret results accurately and seek further medical advice if necessary.
When to test for influenza
Testing during early symptoms
Testing for influenza during the initial stages of illness is crucial. Early symptoms, such as fever, cough, sore throat, and body aches, often resemble other respiratory infections. Identifying the flu virus promptly allows healthcare providers to recommend antiviral treatments, which are most effective within the first 48 hours of symptom onset. Early testing also helps reduce the risk of spreading the virus to others. Tools like the Influenza A/B Rapid Test Kit provide quick results, enabling individuals to confirm their condition and take necessary precautions.
Testing for high-risk groups
Certain individuals face a higher risk of severe complications from influenza. These groups include young children, pregnant women, older adults, and those with chronic medical conditions like asthma or diabetes. Testing is especially important for these populations to ensure timely intervention. Healthcare providers may prioritize molecular assays or rapid tests for high-risk patients to confirm the diagnosis and initiate treatment. Early detection in these groups can prevent hospitalizations and improve outcomes.
When testing may not be necessary
In some cases, testing for influenza may not be required. Individuals with mild symptoms who can recover at home might not need a formal diagnosis. Instead, they can focus on rest, hydration, and over-the-counter remedies. Additionally, during widespread flu outbreaks, healthcare providers may diagnose influenza based on symptoms alone, especially when testing resources are limited. However, those experiencing worsening symptoms or belonging to high-risk groups should seek medical advice.
Testing for influenza A or B ensures accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Various options, such as the Influenza A/B Rapid Test Kit, provide flexibility in speed and accuracy.
Tip: Always consult a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable test and receive expert guidance on managing symptoms or treatment plans.
FAQ
What is the best time to test for influenza A or B?
Testing within the first 48 hours of symptom onset provides the most accurate results. Early testing ensures timely treatment and reduces virus transmission risks.
Can at-home influenza tests replace clinical testing?
At-home tests offer convenience but may lack the accuracy of clinical methods. Confirming results with a healthcare provider ensures proper diagnosis and treatment.
Are influenza tests safe for children?
Yes, influenza tests are safe for children. Healthcare providers use gentle swabbing techniques to collect samples, ensuring minimal discomfort during the procedure.
Post time: Jan-25-2025