SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION THE TEST
Malaria is a mosquito-borne, hemolytic, febrile illness that infects over 200 million people and kills more than 1 million people per year. It is caused by four species of Plasmodium: P. falciparum, P. vivax, P. ovale, and P. malariae. These plasmodia all infect and destroy human erythrocytes, producing chills, fever, anemia, and splenomegaly. P. falciparum causes more sever disease than the other plasmodial species and accounts for most malaria deaths. P. falciparum and P. vivax are the most common pathogens, however, there is considerable geographic variation in species distribution.
Traditionally, malaria is diagnosed by the demonstration of the organisms on Giemsa stained thick smears of peripheral blood, and the different species of plasmodium are distinguished by their appearance in infected erythrocytes. The technique is capable of accurate and reliable diagnosis, but only when performed by skilled microscopists using defined protocols, which presents major obstacles for the remote and poor areas of the world.
The Malaria Pf/Pv Ag Rapid Test is developed for solving these obstacles. It utilizes antibodies specific to P. falciparum Histidine Rich Protein-II (pHRP-II) and to P. vivax Lactate Dehydrogenase (Pv-LDH) to simultaneously detect and differentiate infection with P. falciparum and P. vivax. The test can be performed by untrained or minimally skilled personnel, without laboratory equipment
PRINCIPLE
The Malaria Pf/Pv Ag Rapid Test is a lateral flow chromatographic immunoassay. The strip test components consist of: 1) a burgundy colored conjugate pad containing mouse anti-Pv-LDH antibody conjugated with colloid gold (Pv-LDH-gold conjugates) and mouse anti-pHRP-II antibody conjugated with colloid gold (pHRP-II-gold conjugates), 2) a nitrocellulose membrane strip containing two test bands (Pv and Pf bands) and a control band (C band). The Pv band is pre-coated with another mouse anti-Pv-LDH specific antibody for the detection of Pv infection, the Pf band is precoated with polyclonal anti-pHRP-II antibodies for the detection of Pf infection, and the C band is coated with goat anti-mouse IgG.
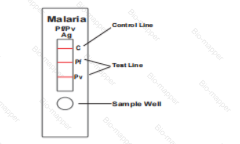
During the assay, an adequate volume of the blood specimen is dispensed into the sample well (S) of the test cassette, a lysis buffer is added to the buffer well (B). The buffer contains a detergent that lyses the red blood cells and releases various antigens, which migrate by capillary action across the strip held in the cassette. Pv-LDH if presents in the specimen will bind to the Pv-LDH-gold conjugates. The immunocomplex is then captured on the membrane by the pre-coated anti-Pv-LDH antibody, forming a burgundy colored Pv band, indicating a Pv positive test result. Alternatively, pHRP-II if presents in the specimen will bind to the pHRP-II-gold conjugates. The immunocomplex is then captured on the membrane by the pre-coated anti-pHRP-II antibodies, forming a burgundy colored Pf band, indicating a Pf positive test result. Absence of any test bands suggests a negative result. The test contains an internal control (C band) which should exhibit a burgundy colored band of the immunocomplex of goat anti- mouse IgG / mouse IgG (anti-Pv-LDH and anti-pHRPII)-gold conjugates regardless of the color development on any of the test bands. Otherwise, the test result is invalid and the specimen must be retested with another device.