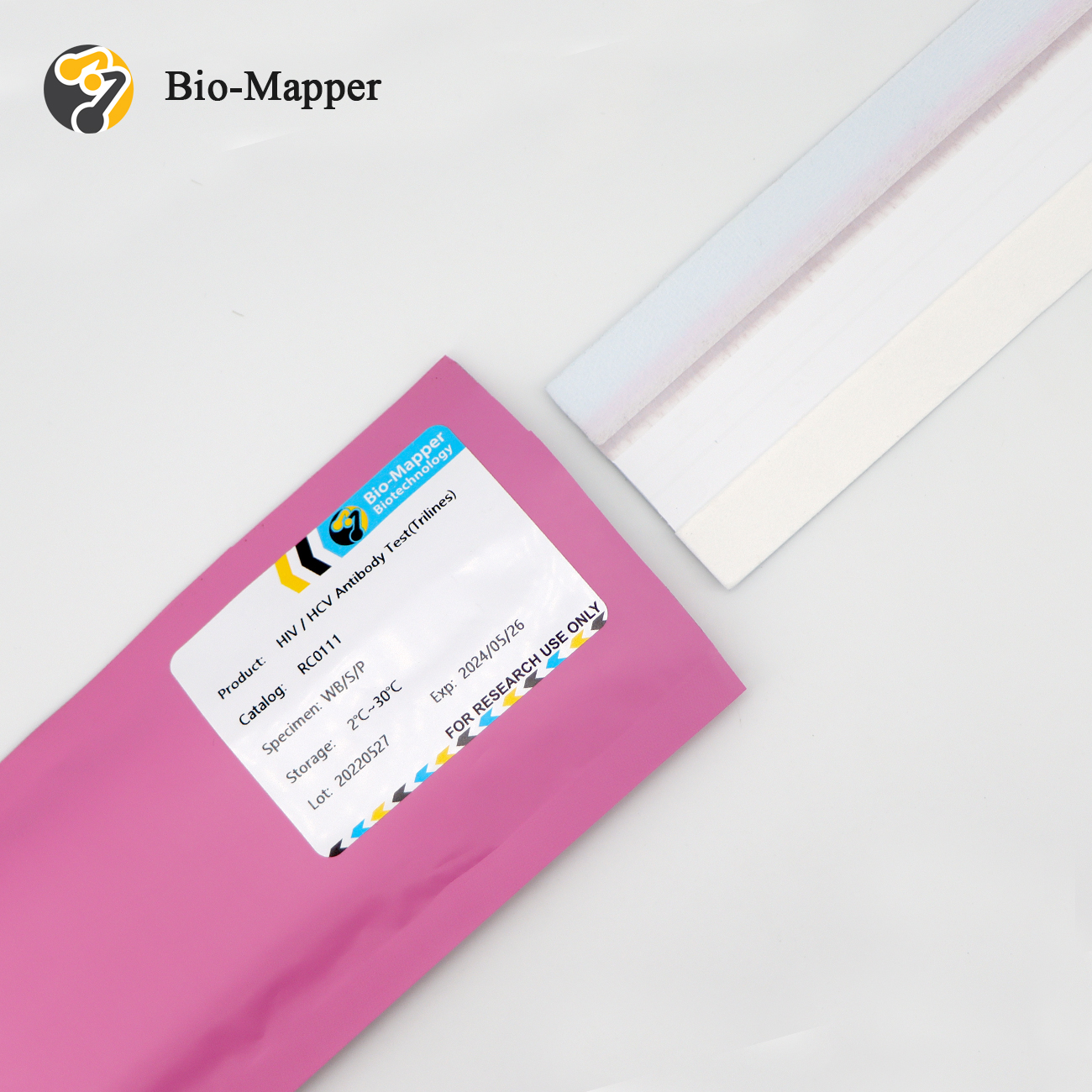
Detailed description
Common methods for AIDS antibody detection are:
1. Pathogen detection
Pathogen detection mainly refers to the direct detection of viruses or viral genes from host samples by virus isolation and culture, electron microscopic morphology observation, virus antigen detection and gene determination. The first two methods are difficult and require special equipment and professional technicians. Therefore, only antigen detection and RT-PCR (reverse transcription PCR) can be used for clinical diagnosis.
2. Antibody detection
HIV antibody in serum is an indirect indicator of HIV infection. According to its main scope of application, the existing HIV antibody detection methods can be divided into screening test and confirmation test.
3. Confirmation reagent
Western blot (WB) is the most commonly used method to confirm the positive serum of screening test. Due to its relatively long window period, poor sensitivity and high cost, this method is only suitable for confirmation test. With the improvement of the sensitivity of the third and fourth generation HIV diagnostic reagents, WB has become increasingly unable to meet the requirements for its use as a confirmatory test.
Another type of screening confirmation reagent approved by FDA is immunofluorescence assay (IFA). IFA costs less than WB, and the operation is relatively simple. The whole process can be completed within 1-1.5 hours. The main disadvantage of this method is that it requires expensive fluorescence detectors and experienced professionals to observe the evaluation results, and the experimental results cannot be preserved for a long time. Now FDA recommends that IFA’s negative or positive results should prevail when issuing the final results to donors whose WB cannot be determined, but it is not regarded as the standard for blood qualification.
4. Screening test
Screening test is mainly used to screen blood donors, so it requires simple operation, low cost, sensitivity and specificity. At present, the main screening method in the world is still ELISA, and there are a few particle agglutination reagents and fast ELISA reagents.
ELISA has high sensitivity and specificity, and is simple to operate. It can be applied only if the laboratory is equipped with a microplate reader and a plate washer. It is especially suitable for large-scale screening in the laboratory.
Particle agglutination test is another simple, convenient and low-cost detection method. The results of this method can be judged by naked eyes, and the sensitivity is very high. It is especially suitable for developing countries or a large number of blood donors. The disadvantage is that fresh samples must be used, and the specificity is poor.
Hepatitis C virus antibody clinical:
1) 80-90% of patients suffering from hepatitis after blood transfusion are hepatitis C, most of them are positive.
2) In patients with hepatitis B, especially those who often use blood products (plasma, whole blood) can cause co infection of hepatitis C virus, making the disease become chronic, liver cirrhosis or liver cancer. Therefore, HCV Ab should be detected in patients with recurrent hepatitis B or patients with chronic hepatitis.